After the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki and the Japanese surrender, the country breathed a collective sigh of relief: the war was over. As the only nation possessing an atomic weapon, there was no concern that America could come under nuclear attack.
That all changed on September 23, 1949, when President Truman made an earth-shaking announcement with these simple words: "We have evidence that within recent weeks an atomic explosion occurred in the U.S.S.R." Almost a month before, on August 29, the Soviet Union had successfully tested an atomic bomb equivalent to the bomb dropped on Nagasaki, Japan almost four years earlier.
An atomic explosion has occurred in Russia - a fateful portent that the Soviets have broken an American A-bomb monopoly on which the non-Communist world depended so heavily.- Los Angeles Times, September 24, 1949
Senior government officials quickly issued low-key statements meant to keep people from panicking.
The calmer the American people take this, the better.... We have anticipated it for four years and it calls for no change in our basic defense plan.- General Omar Bradley, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
Nevertheless, for everyone in the United States, life did change. From the youngest school children, who had to practice "duck and cover" drills in their classrooms, to the president of the United States, who now had to confront the very real possibility of a nuclear war, the Cold War took on an entirely new, and far more dangerous, threat.

Air Raid Siren
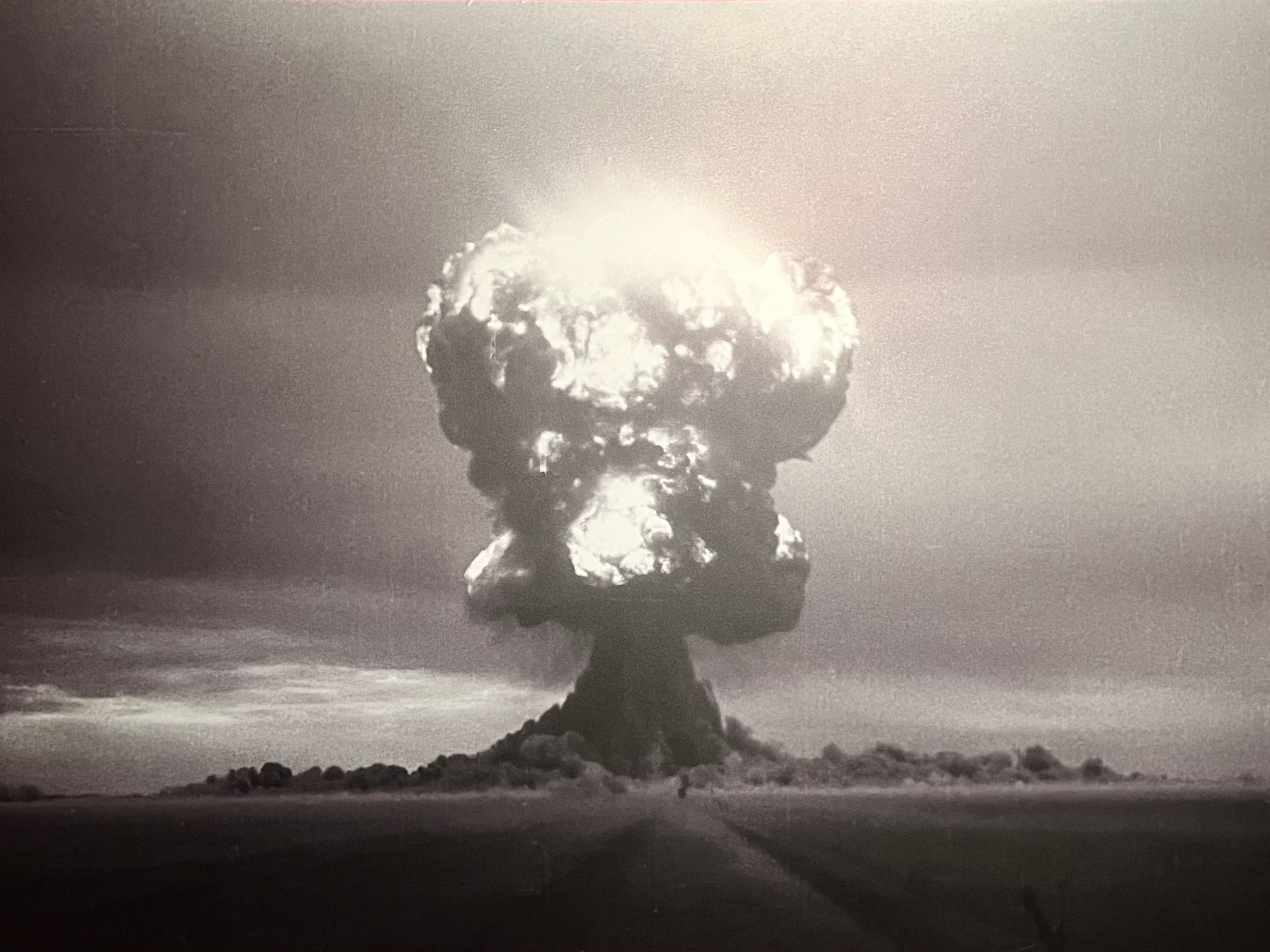

Semipalatinsk Test Site
- The Soviet Union successfully tested their first nuclear weapon in August 1949, in Kazakhstan at the Semipalatinsk Test Site.
I believe the American people, to the fullest extent consistent with national security, are entitled to be informed of all developments in the field of atomic energy. That is my reason for making public the following information:
We have evidence that within recent weeks an atomic explosion occurred in the U.S.S.R.
Ever since atomic energy was first released by man, the eventual development of this new force by other nations was to be expected. This probability has always been taken into account by us.
Nearly four years ago I pointed out that "scientific opinion" appears to be practically unanimous that the essential theoretical knowledge upon which the discovery is based is already widely known.
There is also substantial agreement that foreign research can come abreast of our present theoretical knowledge in time and, in the three-nation declaration of the President of the United States and the Prime Ministers of the United Kingdom and of Canada, dated November 15, 1945, it was emphasized that no single nation could in fact have a monopoly of atomic weapons.
This recent development emphasizes once again, if indeed such emphasis were needed, the necessity for that truly effective enforceable international control of atomic energy which this Government and the large majority of the members of the United Nations support.
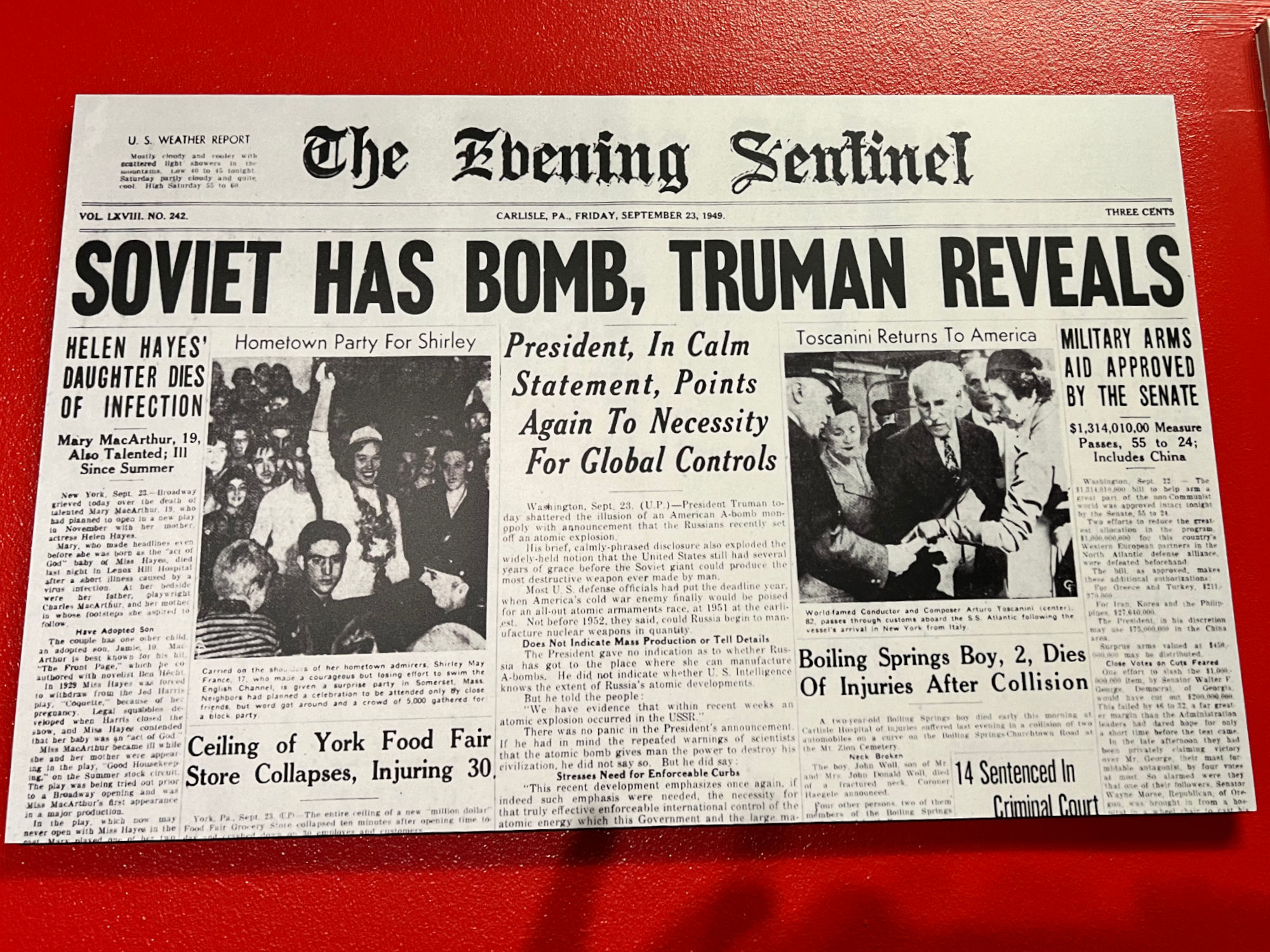
Soviet Has Bomb, Truman Reveals
- Newspapers around the country reported the words of President Truman, who had to inform the American public that the United States no longer had a monopoly on nuclear weapons.

PBSFirst Lightning
The Soviets called their first atomic test "First Lightning." A train belching black smoke, shipped the bomb components 2,000 miles from Arzamas, the weapons laboratory in Russia to the test site at Semipalatinsk in Kazakhstan. Like the Americans, the Soviets constructed a tower from which to test their weapon. They assembled the device in an adjacent concrete hall which had railway trucks running down its entire length. The bomb components came in one end and the completed device was wheeled out the other end to be hoisted to the top of the tower.The Soviets wanted to learn about the effects of nuclear weapons. So in addition to instruments that would measure the size of the shock wave and the intensity of the radiation, they constructed wooden and brick houses, bridges, tunnels and water towers in the vicinity of the tower. They also put caged animals nearby so that they could study the effects of nuclear radiation.
Igor Kurchatov, the scientific director of the soviet nuclear bomb program who was in charge of the test, arrived at the site in May of 1949. In the weeks leading up to the blast he organized two rehearsals so everyone would know exactly what to do on shot day. The chair of the Special Committee on the atomic bomb, Lavrentii Beria, arrived in the middle of August. He observed the assembly work and reported back to Soviet leader Joseph Stalin.
At 2 am on August 29, 1949 the assembled bomb was wheeled to the tower. The blast was scheduled for 6 am. Kurchatov and a handful of other scientists gathered in the command post with Beria and his entourage. They left the door open so they could watch the blast go off . They knew that they would have time to close the door because it would take 30 seconds for the shock wave to reach them. Kurchatov gave the order for the detonation.
An observer from a northern post about nine miles from the blast had one of the best views: "On top of the tower an unbearably bright light blazed up. For a moment or so it dimmed and then with new force began to grow quickly. The white fireball engulfed the tower and the workshop and expanding rapidly, changing color it rushed upwards. The blast wave at the base, sweeping in its path structures, stone houses, machines, rolled like a billow from the center, mixing up stones, logs of wood, pieces of metal and dust into one chaotic mass. The fireball, rising and revolving, turned orange, red. Then dark streaks appeared. Streams of dust, fragments of brick and board were drawn in after it, as into a funnel."
The relief and euphoria in the room was overwhelming. Kurchatov cried out, "It works! It works!" And Iulii Khariton, the scientific director of Arzamas, remembers Beria hugging him. All of the scientists knew that their own personal fates depended on the success of the bomb. One of them later said that if it had failed they would have all been shot. But besides being thankful for their own lives, many of the scientists felt they had contributed to the Soviet Union's security. Khariton later said, "when we succeeded in solving this problem, we felt relief, even happiness -- for in possessing such a weapon we had removed the possibility of its being used against the USSR with impunity."
Beria's own joy temporarily dissipated when his suspicions got the better of him. He put a call through to an observer at the north post who had also witnessed an American test in 1946. "Is it the same as the American one?" Beria wanted to know. "It is," the observer assured him. The bomb had in fact yielded 20 kilotons, making it about the same size as Trinity, the first U.S. atomic test.
History.comCode Name: First Lightning
At a remote test site at Semipalatinsk in Kazakhstan, the USSR successfully detonates its first atomic bomb, code name “First Lightning.” In order to measure the effects of the blast, the Soviet scientists constructed buildings, bridges, and other civilian structures in the vicinity of the bomb. They also placed animals in cages nearby so that they could test the effects of nuclear radiation on human-like mammals. The atomic explosion, which at 20 kilotons was roughly equal to “Trinity,” the first U.S. atomic explosion, destroyed those structures and incinerated the animals.On September 3, a U.S. spy plane flying off the coast of Siberia picked up the first evidence of radioactivity from the explosion. Later that month, President Harry S. Truman announced to the American people that the Soviets too had the bomb.
Three months later, Klaus Fuchs, a German-born physicist who had helped the United States build its first atomic bombs, was arrested for passing nuclear secrets to the Soviets. While stationed at U.S. atomic development headquarters during World War II, Fuchs had given the Soviets precise information about the U.S. atomic program, including a blueprint of the "Fat Man" atomic bomb later dropped on Japan, and everything the Los Alamos scientists knew about the hypothesized hydrogen bomb. The revelations of Fuchs' espionage, coupled with the loss of U.S. atomic supremacy, led President Truman to order development of the hydrogen bomb, a weapon theorized to be hundreds of times more powerful than the atomic bombs dropped on Japan.
On November 1, 1952, the United States successfully detonated “Mike,” the world's first hydrogen bomb, on the Elugelab Atoll in the Pacific Marshall Islands. The 10.4-megaton thermonuclear device instantly vaporized an entire island and left behind a crater more than a mile wide. Three years later, on November 22, 1955, the Soviet Union detonated its first hydrogen bomb on the same principle of radiation implosion. Both superpowers were now in possession of the so-called “superbomb,” and the world lived under the threat of thermonuclear war for the first time in history.
WIKIPEDIASoviet Atomic Bomb Project
The classified research and development program that was authorized by Joseph Stalin in the Soviet Union to develop nuclear weapons during and after World War II.Although the Soviet scientific community discussed the possibility of an atomic bomb throughout the 1930s, going as far as making a concrete proposal to develop such a weapon in 1940, the full-scale program was not initiated and prioritized until Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union.
Because of the conspicuous silence of the scientific publications on the subject of nuclear fission by German, American, and British scientists, Russian physicist Georgy Flyorov suspected that the Allied powers had secretly been developing a "superweapon" since 1939. Flyorov wrote a letter to Stalin urging him to start this program in 1942. Initial efforts were slowed due to the German invasion of the Soviet Union and remained largely composed of the intelligence gathering from the Soviet spy rings working in the U.S. Manhattan Project.
After Stalin learned of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the program was pursued aggressively and accelerated through effective intelligence gathering about the German nuclear weapon project and the American Manhattan Project. The Soviet efforts also rounded up captured German scientists to join their program, and relied on knowledge passed by spies to Soviet intelligence agencies.
On 29 August 1949, the Soviet Union secretly conducted its first successful weapon test (First Lightning, based on the American "Fat Man" design) at the Semipalatinsk-21 in Kazakhstan. Stalin alongside Soviet political officials and scientists were elated at the successful test. A nuclear armed Soviet Union sent its rival Western neighbors, and particularly the United States into a state of unprecedented trepidation.
WIKIPEDIAFrom 1949 Onwards
The Soviet Union manufactured and tested nuclear weapons on a large scale. The nuclear capabilities these tests helped develop were crucial to projecting and maintaining its global status. In total, the Soviet Union conducted 715 nuclear weapon tests throughout the course of the Cold War. Furthermore, the nuclear capabilities of the Soviet Union escalated the Cold War with the United States to the possibility of nuclear war and ushered in the doctrine of mutually assured destruction.